10 Common Network Issues and How to Fix Them
Internet errors are common encounters in our web experiences. Numerous times, you go online to work or get important information, and then, boom, an error notification pops up.
At times, frustration sets in, leading to abandonment of the task at hand. This can be incredibly disheartening.
If you have faced such experiences before and found yourself stuck without knowing what to do next, fret no more.
Today, we will explore ten common network issues and provide easy solutions to fix them.
Get ready to equip yourself with this valuable knowledge.
10 Common Network Issues and How to Fix Them
1. DNS Errors
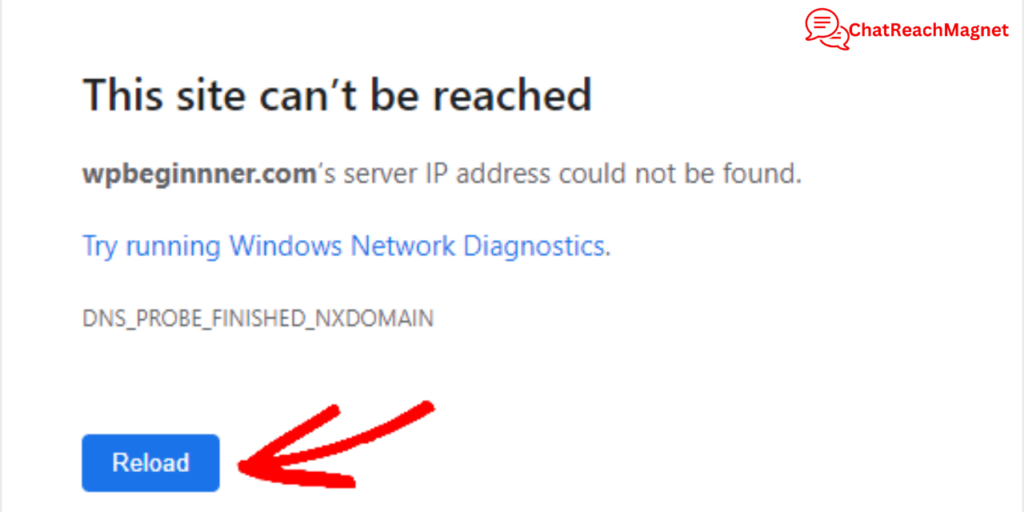
DNS (Domain Name System) errors are among the most frequent issues internet users face.
A common example is the dreaded “DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN” error, which indicates that the DNS cannot resolve the domain name.
How to Fix:
- Restart your router and computer to refresh the network connection.
- Check your DNS settings. Consider switching to public DNS servers like Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1).
- Clear your DNS cache using the following command in the terminal:
ipconfig /flushdns - Ensure your internet service provider (ISP) is operational.
Get More Information on How to Fix the DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN Error
here.
2. Slow Internet Speeds
Slow internet speeds can make browsing, streaming, or working online unbearable. This issue may result from high network congestion, outdated hardware, or bandwidth throttling by your ISP.
How to Fix:
- Check your internet speed using tools like Speedtest.net.
- Reboot your modem and router.
- Limit the number of connected devices using the network.
- Ensure your router firmware is updated.
- Contact your ISP to rule out network throttling.
3. Wi-Fi Signal Drops
Frequent Wi-Fi disconnections can occur due to interference, router placement, or outdated firmware.
How to Fix:
- Move your router to a central location, away from walls and electronic devices.
- Change the Wi-Fi channel to reduce interference. Most routers allow you to do this in their settings.
- Upgrade your router firmware to the latest version.
- Consider investing in a Wi-Fi extender for larger spaces.
4. IP Address Conflicts

When two devices on the same network share the same IP address, an IP conflict arises, leading to connectivity issues.
How to Fix:
- Restart your router to assign new IP addresses automatically.
- Manually set unique static IP addresses for devices.
On Windows, you can release and renew the IP address using these commands in the Command Prompt:
ipconfig /release
- ipconfig /renew
5. No Internet Connection
You may find that your device is connected to the Wi-Fi, but there is no internet access.
This can be due to ISP issues or incorrect network settings.
How to Fix:
- Check if other devices on the same network have internet access. If not, the issue might be with the ISP.
- Restart your modem and router.
- Verify that your device’s network adapter is functioning correctly. Update the adapter drivers if needed.
- Disable and re-enable your network connection.
6. Unresponsive Router
A router that freezes or becomes unresponsive can disrupt your network connectivity.
How to Fix:
- Perform a power cycle by unplugging the router, waiting for 10 seconds, and plugging it back in.
- Reset the router to factory settings using the reset button. Reconfigure your settings afterward.
- Ensure the router’s firmware is up-to-date.
- If the issue persists, consider replacing the router.
7. VPN Connection Issues

VPN (Virtual Private Network) problems include inability to connect, slow speeds, or dropped connections.
How to Fix:
- Ensure your VPN app is updated to the latest version.
- Switch to a different server within your VPN application.
- Disable the firewall or antivirus temporarily to check if they are blocking the connection.
- Check your internet speed to ensure it is sufficient for VPN use.
- Contact your VPN provider’s support for further troubleshooting.
8. Network Timeouts
Network timeouts occur when a server takes too long to respond, often caused by heavy traffic or poor connectivity.
How to Fix:
- Refresh the page or try accessing the site after a few minutes.
- Restart your router to improve connectivity.
- Use a wired connection for more stable access.
- Clear your browser’s cache and cookies.
- Test your connection with another device to rule out device-specific issues.
9. Firewall Blocking Connections
Sometimes, your firewall might block legitimate connections, leading to restricted network access.
How to Fix:
- Check your firewall settings to ensure the required applications or websites are allowed.
- Temporarily disable the firewall to determine if it is the cause of the issue.
- Reconfigure firewall rules to permit necessary traffic.
- Ensure your firewall software is up-to-date.
10. Overloaded Network
An overloaded network occurs when too many devices are connected, leading to reduced speeds or connectivity drops.
How to Fix:
- Disconnect unused devices from the network.
- Set bandwidth limits for devices that consume excessive data.
- Upgrade to a higher-speed internet plan if necessary.
- Use Quality of Service (QoS) settings in your router to prioritise certain types of traffic, such as streaming or gaming.
Conclusion
Network issues can be a major source of frustration, but understanding the causes and solutions can help you navigate them with ease.
From DNS errors to overloaded networks, these ten common problems often have simple fixes that require only a few minutes of your time.
Implementing these troubleshooting steps, you can ensure a smoother and more reliable internet experience. Happy browsing

